Step into a Pain-Free Future with Stem Cell Treatment for Knee Injuries
A knee injury refers to damage or trauma that affects the structures within or surrounding the knee joint. The knee joint is a complex hinge joint that connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia) and allows for flexion, extension, and limited rotation of the leg. Knee injuries can occur due to various reasons, including sports activities, accidents, overuse, or underlying medical conditions.
Symptoms of a knee injury may include pain, swelling, stiffness, instability, difficulty bearing weight, popping or clicking sensations, and limited range of motion. Diagnosis often involves a physical examination, medical history review, imaging tests (X-rays, MRI), and sometimes arthroscopy (a minimally invasive procedure).
Knee injuries can have various effects on the affected individual, ranging from temporary discomfort to long-term consequences. The specific effects of a knee injury can depend on the type and severity of the injury, as well as the individual’s overall health and activity level.
Prevention of knee injuries can be promoted through proper warm-up and stretching before physical activity, maintaining strong and flexible leg muscles and using appropriate footwear.
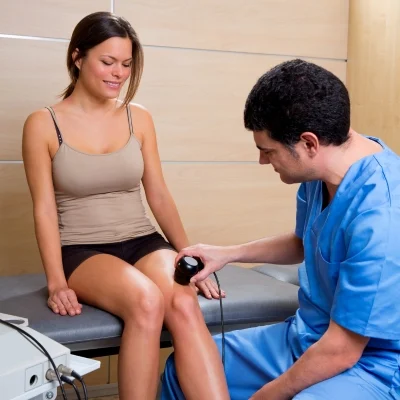

Benefits of Stem Cell Treatment for Knee Injury
- Enhanced Healing: Stem cells can differentiate into various cell types, promoting the repair of damaged cartilage, tendons, and ligaments.
- Pain Reduction: By reducing inflammation and promoting tissue repair, stem cell therapy can help alleviate chronic pain associated with knee injuries.
- Minimally Invasive: The procedure is typically less invasive than surgical options, involving injections rather than extensive surgery.
- Shorter Recovery Time: Patients often experience faster recovery compared to traditional surgical methods, allowing them to return to normal activities sooner.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: Lower risk of complications and infections compared to surgical interventions.
Procedure of Stem Cell Therapy for Knee Injuries
Patient Evaluation
A medical professional will assess the patient’s condition to determine if stem cell therapy is a suitable treatment option. This assessment might include physical examinations, patient medical history review, and imaging studies such as MRI or X-ray.
Stem Cell Harvesting
If the patient is a suitable candidate for the procedure, stem cells will be harvested from the patient’s body. This is typically done through a bone marrow aspiration from the hip or through adipose (fat) tissue extraction. The harvesting process is usually performed under local anesthesia to minimize discomfort.
Stem Cell Processing
The harvested material is then processed in a laboratory to isolate the stem cells. If bone marrow is used, a centrifuge is used to separate the stem cells from other cells. If adipose tissue is used, it first needs to be processed to break down the fat cells and isolate the stem cells.
Concentration
The isolated stem cells are concentrated into a small volume. This increases the number of stem cells that can be injected into the knee, potentially improving the effectiveness of the treatment.
Injection
The concentrated stem cells are injected into the patient’s knee using ultrasound or fluoroscopic (X-ray) guidance to ensure accurate placement. This is typically performed under local anesthesia.
Post-Treatment Care
Post-treatment care instructions may include rest, physical therapy, or other rehabilitation exercises to help the knee heal. The patient will be scheduled for follow-up appointments to monitor the healing process and assess the effectiveness of the treatment.
Best Knee treatment Hospitals in the World
America, Guadalajara, Mexico
America, Guadalajara, Mexico
Mexico, America, Nuevo Progresso
Regenerative Medicine Packages for Knee Injuries
Stem Cell Therapy for Knees Success Stories
Are you tired of living with chronic knee pain, limited mobility, and a decreased quality of life? Imagine a future where you can enjoy your favorite activities, walk pain-free, and regain your independence. Don’t let knee pain limit your potential for an active and fulfilling life. Embrace the regenerative power of stem cell therapy with PlacidWay and unlock a future of improved knee health. Contact us now, and let your knees soar once again!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the success rate of stem cell therapy for knees?
The success rate of stem cell therapy for knees can vary depending on several factors, including the specific condition being treated, the severity of the condition, the patient’s overall health, and the expertise of the medical team performing the procedure. It’s important to note that stem cell therapy is still a relatively new field, and research is ongoing to determine its long-term effectiveness.
Can stem cell therapy repair damaged knees?
Stem cell therapy has shown promising potential for repairing damaged knees, particularly in cases of certain knee conditions and injuries. The use of stem cells aims to stimulate the body’s natural healing mechanisms and promote tissue regeneration.
In the context of knee damage, stem cell therapy may be used to target various issues, including:
- Osteoarthritis: Stem cells can help alleviate the symptoms of osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that causes cartilage breakdown and joint inflammation. By introducing stem cells into the affected area, it is believed that they can promote cartilage regeneration and reduce inflammation, potentially leading to pain relief and improved joint function.
- Ligament and Tendon Injuries: Stem cell therapy has shown promise in the treatment of ligament and tendon injuries, such as ACL tears or rotator cuff tears. Stem cells can potentially aid in the regeneration of damaged ligament or tendon tissue, enhancing the healing process and improving overall tissue integrity.
- Cartilage Damage: Stem cells have the ability to differentiate into various cell types, including chondrocytes, which are the cells that make up cartilage. This property makes stem cell therapy a potential option for repairing cartilage damage in the knee joint, such as focal defects or lesions.
How long does stem cell therapy last for knees?
The duration of the effects of stem cell therapy for knees can vary from patient to patient. Since stem cell therapy is a relatively new field, the long-term data on the durability of the treatment is still limited. However, research and clinical experience suggest that the benefits of stem cell therapy can be long-lasting for some individuals.
Can stem cells regrow joints?
The ability of stem cells to regrow or completely replace joints is still an area of ongoing research and development. While stem cell therapy holds promise for promoting tissue regeneration and repair, it is important to clarify that the complete regrowth of a joint, such as a knee joint, is a complex process that may require more than just stem cells.
Stem cells have the remarkable potential to differentiate into various cell types, including those found in joint tissues such as cartilage, ligaments, and tendons. This ability has led to the exploration of using stem cells to repair and regenerate damaged joint tissues.
Is stem cell better than surgery?
Whether stem cell therapy is better than surgery or vice versa depends on several factors, including the specific condition being treated, the individual patient’s circumstances, and the recommendations of medical professionals. It’s important to understand that stem cell therapy and surgery are different approaches with their own advantages and limitations.
Stem cell therapy:
- Non-invasive or minimally invasive: Stem cell therapy is typically performed through injections, which are less invasive than traditional surgical procedures. This can result in shorter recovery times, reduced scarring, and a lower risk of complications.
- Tissue regeneration potential: Stem cells have the ability to differentiate into various cell types, including those found in damaged tissues. The goal of stem cell therapy is to promote tissue regeneration and repair, potentially restoring function and reducing pain.
- Potential for joint preservation: In some cases, stem cell therapy may help preserve the joint and delay or prevent the need for surgery. It can be particularly beneficial for early-stage conditions or injuries where surgical intervention may not be immediately necessary.
Surgery:
- Definitive treatment for certain conditions: In cases where significant joint damage or structural abnormalities are present, surgery may be the most effective option. Procedures like joint replacement, ligament reconstruction, or cartilage repair surgeries can provide long-term solutions for certain conditions.
- Immediate correction: Surgery can address specific issues, such as repairing torn ligaments, removing damaged tissues, or realigning joint structures, in a more direct and immediate manner.
- Well-established procedures: Surgical interventions have been extensively researched and refined over time, with well-documented success rates for specific conditions and predictable outcomes.
Request Free Quote